Physical Vapor Deposition - PVD
The term Physical Vapor Deposition describes several vacuum deposition techniques to coat substrates with thin films by the condensation of a vaporized form of the desired film material. In contrast to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) where chemical reactions are used to coat the substrates , in PVD only physical processes are utilized such as:
- Electron beam evaporation
- Evaporation
- Cathodic Arc deposition
- Sputter deposition
- Pulsed laser deposition
Sputter deposition
In sputter deposition a magnetically enhanced glow discharge is used to bombard the material that is subsequently sputtered away for deposition. The eject atoms tend to deposit on all surface inside the vacuum chamber, a substrate place inside the chamber will be coated with a thin film consisting out of the target material. The target material erodes from the target onto a substrate depositing a thin film there.
Fundamentals of Sputtering
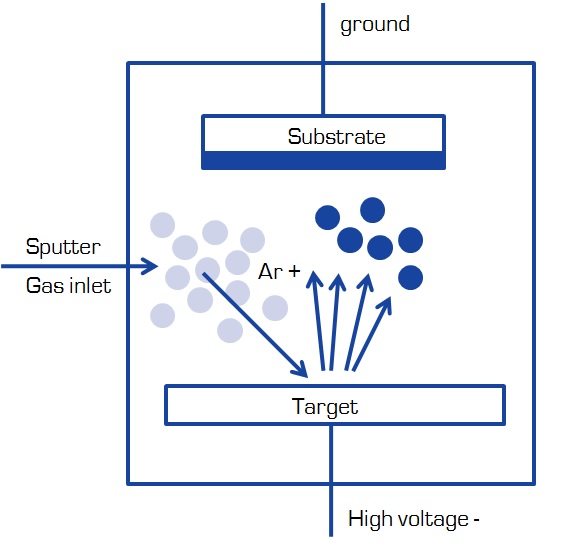
Sputtering is a phenomena where atoms are ejected from a target material due to bombardment of the target by energetic particles. This process is based on the generation of a glow discharge between two electrodes in a confined vacuum chamber. To generate the discharge the chamber is pumped down to a base pressure of 10-4 Pa or below and a sputter gas, usually argon is introduced into the chamber. When a sufficiently high DC voltage is applied between the two electrons the sputter gas gets partially ionized and the electrical discharge forms. Ions are accelerated towards the target which functions as a cathode ejecting atoms from the target material and secondary electrons and the discharge rapidly evolves into a steady state.